Hormonal imbalance and its effect on hair loss and health; most common causes that lead to hormonal imbalance

In reality, there are many factors that can lead to hair loss, such as diseases affecting hair health, including hereditary conditions, skin disorders, autoimmune diseases affecting the scalp, and others. One of the most common reasons for hair loss in women, in particular, is hormonal imbalances in the body. These imbalances can affect the hair's lifecycle, making hair follicles fragile, weak, and prone to significant hair loss. In this article, we'll explore the most important organic conditions that disrupt hormonal balance in the body and how they impact hair health, leading to hair loss.
How do hormones affect hair follicles in the body?
The different hormones in the body, especially androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, have a significant impact on the hair's lifecycle and the structure of hair follicles. Androgens affect hair follicles depending on the location of the hair on the body. For example, some studies have shown that androgens stimulate hair growth in certain areas of the body, but they have no effect on areas like eyelash follicles. Any disruption in these hormones, for any reason, can result in hair growth problems and hair loss. In fact, other hormones also influence hair growth, and any disturbance in their regulation can negatively affect hair health. These hormones include:
- Prolactin
- Estradiol
- Progesterone
- Thyroid hormones
- Melatonin
- Cortisol
The most common causes of hair loss due to hormonal imbalances include:
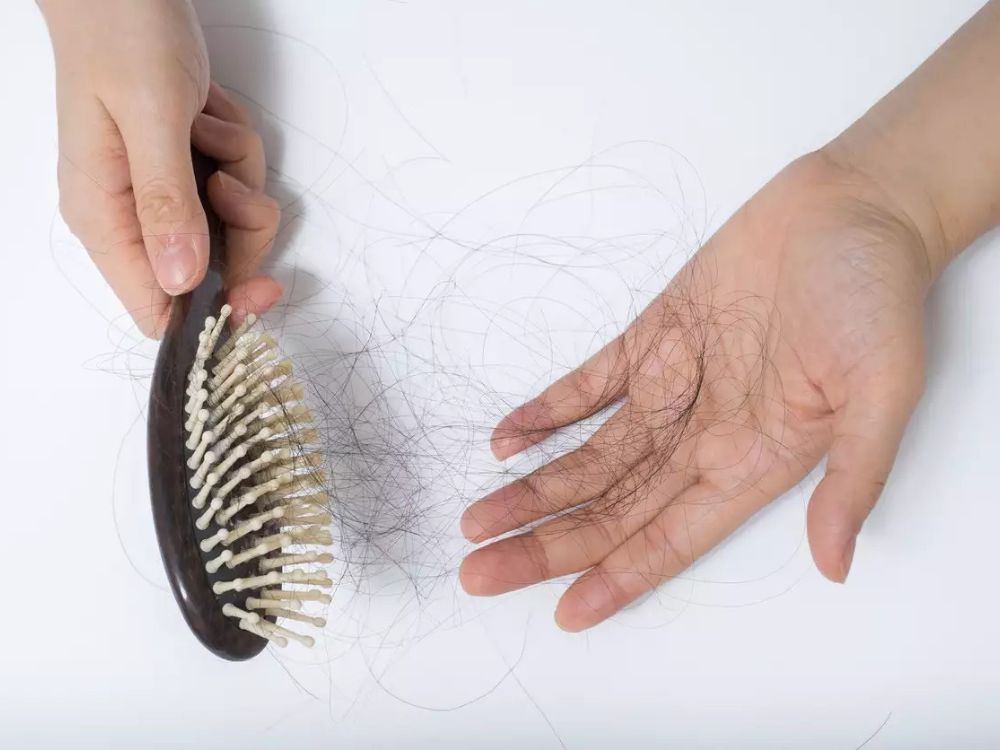

Hormones naturally fluctuate throughout life, but when these disruptions occur frequently, you'll likely notice clear symptoms in your body, particularly in your hair. If your hormones become imbalanced, you might notice that your hair has become dry and brittle. This can happen if your thyroid gland is underactive or inactive. Sometimes, your hair may appear scattered and thin. This can also occur if you have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition characterized by excessive inflammation and changes in estrogen hormones, affecting hair growth.
Additionally, factors such as childbirth, menopause, and the premenopausal stage can contribute to hair loss because all these conditions are associated with a decrease in estrogen levels. This reduction in estrogen can lead to hair loss. Here are some of the most common reasons for hair loss due to various hormonal imbalances:
1. Thyroid Dysfunction

Hypothyroidism, or an underactive thyroid, is one of the most common thyroid disorders and can lead to hair loss. The thyroid gland produces the primary hormone that affects the function of various tissues in the body, including hair follicles. Healthy levels of T4, a thyroid hormone, are essential for hair growth.
A deficiency in this hormone can make hair follicles spend less time in the growth phase, disrupting the hair renewal cycle and leading to hair loss. Hair loss due to thyroid dysfunction is usually uniform across the entire scalp, with scattered or thinning hair. If you're experiencing fatigue, dry skin, or difficulty in losing weight, it's essential to consult an endocrinologist for the necessary tests and a thyroid evaluation.
2. Hormonal Changes After Childbirth

More specifically, during the postpartum period, pregnancy alters the natural hair growth cycle and prevents the usual hair loss during pregnancy, resulting in a thick head of hair. However, after giving birth, many hormones, including estrogen, drop rapidly. These changes also disrupt mood, metabolism, and sleep patterns, causing a hormonal imbalance in the body, which triggers the shedding of all the hair that didn't fall out during pregnancy all at once. You may find your shower and hairbrush filled with hair.
But don't worry, postpartum hair loss is entirely normal, and the good news is that it's temporary. Typically, it peaks around two to five months after giving birth, and your hair will eventually return to its natural balance. Nonetheless, it's essential to ensure you're consuming an adequate amount of high-quality proteins, healthy fats, and sufficient calories to replenish essential nutrients and support the growth of healthy hair.
3. Menopause

Another type of hair loss occurs due to changes in estrogen levels during menopause and perimenopause. Menopause is defined as the absence of a menstrual period for a full year, but before this time, many women experience a transitional phase known as perimenopause. This phase can bring side effects such as weight gain, mood swings, and hair loss. As your body transitions into menopause, your ovaries gradually cease estrogen production, a key hormone necessary for hair health. Simultaneously, other glands take over a small amount of estrogen production, which remains essential for basic bodily functions.
4. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Hormonal imbalance is a distinctive feature of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Inflammation and increased insulin secretion in PCOS lead to ovarian changes, affecting the ovulation process and disrupting the body's hormone balance. This, in turn, causes hair to grow in places where it doesn't typically grow in women, such as the face and chin, while simultaneously leading to hair thinning and loss in the areas where it usually grows. If you're experiencing hair loss due to PCOS, you may notice hair thinning, especially around the crown of your head. This is because the ovaries overproduce androgens, which are male hormones like testosterone. High androgen levels can shrink hair follicles and shorten their growth cycle.
Can hair regrow after correcting hormonal imbalances in the body?
The good news about hormonal hair loss is that it can often be reversed by addressing the underlying hormone issues. Since hair loss or thinning is a side effect of an underlying condition, once the root cause is corrected, your hair can return to its normal state. However, during the period of hair loss and while waiting for the cause to be identified and addressed, there are ways you can help balance your hormones and reverse the shedding process, including:
- Following a diet rich in nutrients necessary for hair health and growth.
- Managing stress and emotional well-being to reduce hormonal fluctuations.
- Trying hair extensions to conceal hair loss while waiting for improvements in your condition.
- Taking proper care of your hair, treating it gently to prevent further hair loss.